一、 What is color
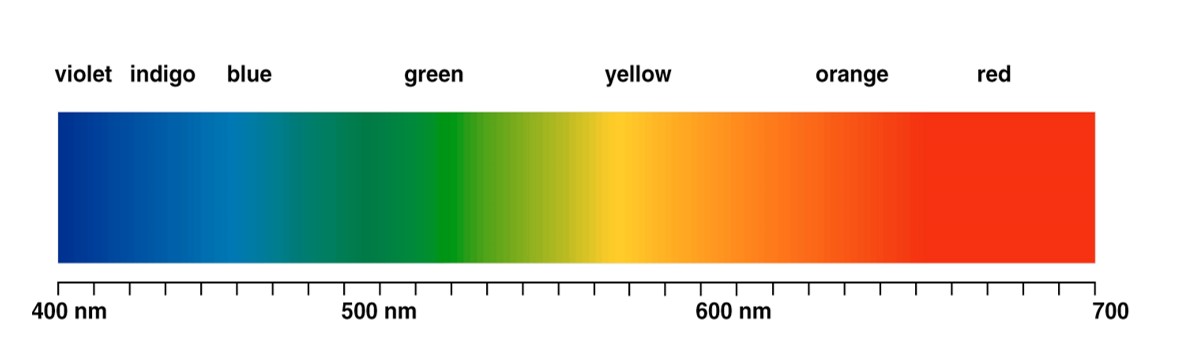
From the perspective of physics, color is the result of human visual system's perception of visible light. The perceived color is determined by the frequency of light wave. Light wave is an electromagnetic radiation with a certain frequency range. The wavelength that human eyes can perceive is between 380 ~ 780nm.
The color in the field of physics is usually defined by the wavelength of light, and the defined color is called Spectral color.
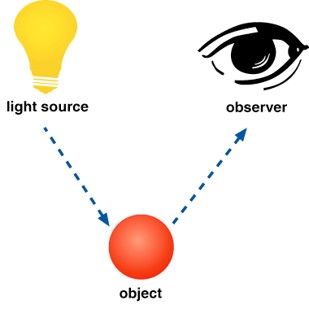
There are three factors that can affect the perception of color:
1. Light source;2 Objects to be seen;3 Observer (person)
Color perception
- The radiant energy of light source and the reflection of objects belong to the category of physics, while the brain and eyes are the content of physiological research, but color is always based on physics, and color perception always contains the reflection of the psychological and physiological effects of color, which makes people have a series of comparison and Association.
- The American Committee on chromaticity defines color as: color is a characteristic of light other than spatial and temporal heterogeneity, that is, the radiation of light can stimulate the retina and cause the scene obtained by the observer through vision.
二、 Introduction to CIE color system
Two important meetings of CIE
- Cambridge Conference in 1931
- Reasons for the conference:
- RGB model adopts physical three primary colors with clear physical meaning, but it is a device related color model (each device has different definitions when using RGB model, which is very non universal)
- • Based on the RGB model, CIE scientists try to use mathematical methods to deduce the theoretical three primary colors from the real primary colors, and create a new color system, so that the pigment, dye and printing industry can clearly formulate the color of products
- Achievement of the conference:
- The standard observer (the response of ordinary human eyes to color) is defined. The standard adopts the imaginary three primary colors of X, y and Z
- Defines Standard Illuminants (a light source specification used to compare colors)
- CIE XYZ primary color system (imaginary primary color system related to RGB) is defined
- CIE xyY color space is defined (a color space derived from XYZ, which separates x and y related to color attributes from brightness Y related to lightness)
- The CIE chromaticity diagram is defined, which is easy to see the relationship between colors
- Reasons for the conference:
- Conference in 1931
- Reasons for the conference:
- • The lightness and chromaticity used in CIE 1931 can not explain the relationship between physical stimulation and color perception.
- The distance between the XYZ system and the two colors represented on the chromaticity diagram is inconsistent with the perceived change of the color observer. This problem is called the perceptual uniformity problem, that is, the difference between the medium value in the color difference is inconsistent with the visual perception.
- To solve the perceptual consistency problem of color space.
- Achievement of the conference:
- • Two color spaces are specified: CIELUV (for self-illumination) and CIELAB (for non self-illumination).
- Reasons for the conference:
Post time: Mar-21-2023