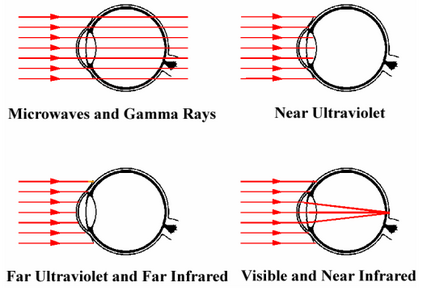
In the past, there was no detailed measurement and evaluation method for the harm caused by light radiation to human body. The traditional test method is to evaluate the content of ultraviolet or invisible light contained in the light wave. Therefore, when the new LED lighting technology appears, we can only use the same standard IEC / EN 60825 as the evaluation of laser products. IEC / EN 60825 mainly tests and calculates the energy of single wavelength light. Now LED is a wide band light, so the Standard IEC / EN 60825 is no longer applicable for lighting. Therefore, IEC has formulated IEC / EN 62471 for risk rating.
The purpose of IEC /EN62471 is to evaluate the light radiation hazards related to different lamps and lamp systems, comprehensively replace the requirements on the energy level of LED products in IEC / EN60825 standard, add photobiological requirements, including radiation intensity, radiation brightness, etc., and classify the products according to the test data, including:
No danger; Class Ⅰ hazard (low risk); Class Ⅱ hazard (moderate risk); Class Ⅲhazard (high risk)
Exemption level (no risk): it will not cause any photobiological radiation hazard under the limit conditions specified in this standard.
Class I (low risk): under normal use conditions, it will not cause photobiological radiation hazards according to people's normal lighting behavior.
Class II (moderate risk): according to the dazzling avoidance of human eyes to high brightness light sources or the uncomfortable response of thermal radiation, it will not cause photobiological radiation hazards.
Class III (high risk): even instantaneous illumination will cause radiation hazard.
The EU standard EN62471:2008 has been implemented since September 1, 2009, and the LED part of EN60825 will be completely invalid on September 1, 2010.
EN 62471 is covered by the CE Low Voltage Directive (LVD Directive 2006 / 95 / EC) and the artificial light radiation directive (AORD 2006 / 25).
IEC / EN 62471 is applicable to all lamps and lamp systems, including LEDs, incandescent bulbs, fluorescent lamps, gas discharge lamps, arc lamps and other lamps and lamps.
EU regulation 244 / 2009 on the energy efficiency requirements of household non directional lamps also specifies that the test on UV radiation needs to be carried out in accordance with IEC / EN 62471 (mainly for energy-saving lamps).
CB certification of self-rectifying LED lamps must include testing of photobiological safety in accordance with IEC 62471 and IEC TR 62471-2. According to OSM / CTL resolution, LED lamps must be tested according to IEC /EN 62471. The label of LED module for human eye protection shall refer to IEC / EN62471
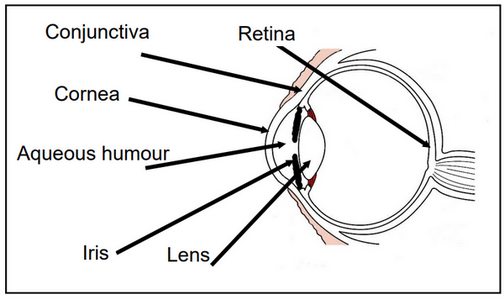
Negative effects of photobiological safety on human eyes / skin
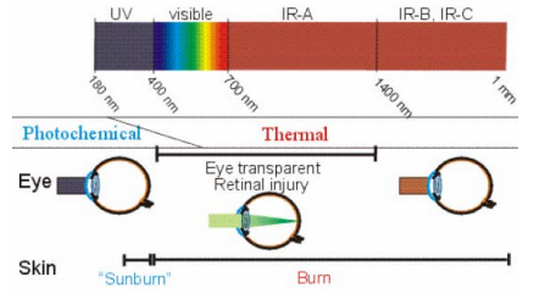
- Negative effects of ultraviolet light on human eyes / skin
To eye
1) Cataract: spectral range 180 – 200 nm to 400 – 420 nm in particular 290 nm to 325 nm
2)Conjunctivitis: spectral range 180 – 200 nm to 400 – 420 nm in particular 200 nm to 320 nm
3)Keratitis: spectral range 180 – 200 nm to 400 – 420 nm
To skin
4)Erythema: spectral range 180-200 nm to 400-420 nm in particular 200 nm to 320 nm
5) Skin elastic tissue degeneration
6) Skin cancer
- Negative effects of visible and infrared light on human eyes / skin
To eye
1) Retinitis (blue light injury): spectral range 300 nm to 700 nm in particular 400 to 500 nm 2) Retinal thermal injury: spectral range 380 nm to 1400 nm
3) Infrared cataract: spectral range 780 nm to 3000 nm
4) Anterior Aqueous humour evaporation: spectral range 1400 nm to 3000 nm
5) Corneal burn: spectral range 1400 nm to 3000 nm
To Skin
6) Skin burn: pectral range 380 nm to 3000 nm
C. Negative effects of light radiation in light on human eyes / skin
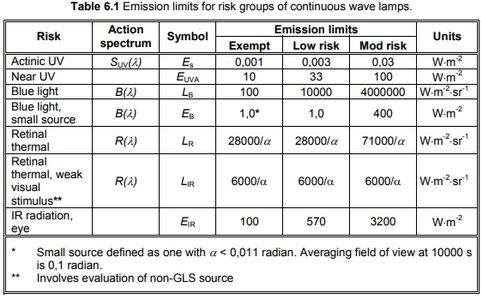
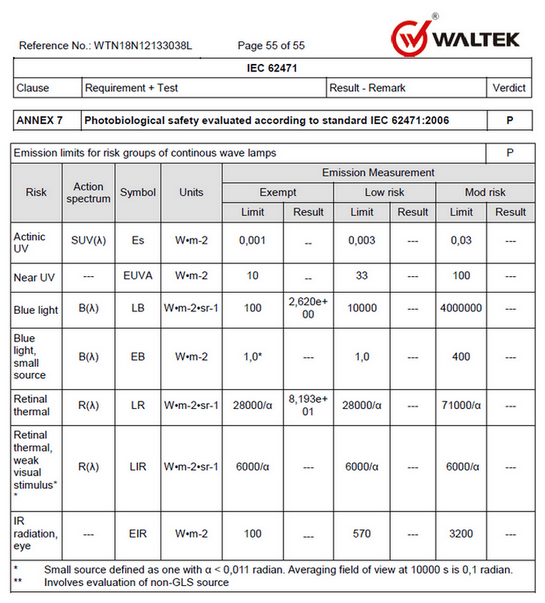
The following is the classification limit table of IEC62471 for photobiological risk:
EN62471 and IEC62471 have slightly different classification limits for photobiological risk, as follows:
1. According to EN62471:2008, the ultraviolet wavelength starts from 180nm, while according to IEC62471:2006, the ultraviolet wavelength starts from 200nm;
2、The S(λ) value of EN62471:2008 is listed in 1nm steps, while IEC62471:2006 is listed in 5nm steps;
3. For the near ultraviolet risk assessment, the limit of Class 0 hazard (no risk) of UVA irradiance is 0,33w / m-2 according to EN62471:2008 standard, while the limit of Class 0 hazard (no risk) of UVA irradiance according to IEC62471:2006 standard is 10,0w / m-2;
4. For the blue light risk: small light source risk assessment (300 – 700nm), the limit of Class 0 hazard (no risk) according to EN62471:2008 is 0,01w / m-2, while the limit of Class 0 hazard (no risk) according to IEC62471:2006 is 1,0w / m-2.
According to IEC / EN 62471, optical radiation sources are grouped according to their potential photobiological risks. It is very important and beneficial for people to classify the light sources that produce light radiation. If the light source is classified as a "safety" group (exemption group) or a low-risk group (risk group I), there is no need for a detailed and in most cases of expensive workplace assessment because it has no Photobiological Safety Risks.
Wellway adopts internationally famous brand LED lamp beads, and the LED moist-proof lamps, LED bracket lamps, LED dust-proof lamps, panel lamps, grille lamps, etc. produced by Wellway can fully meet the requirements of customers for EN62471:2008 standard. The photobiological safety testing of lamp beads and lamps are all passed through by third-party testing agency.
(Part of the content comes from https://www.iec.ch/, if there is infringement, please contact and delete it immediately)
(Some pictures come from the Internet. If there is infringement, please contact us and delete them immediately)
Post time: May-23-2022